The Potential Of Blockchain To Disrupt The Agriculture Industry
The agricultural industry, a cornerstone of global economies, is ripe for disruption. Traditional methods are plagued by inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and vulnerability to fraud. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, presents a powerful solution to address these challenges. From supply chain management to financial inclusion, blockchain holds the potential to revolutionize how we produce, trade, and consume food.
Introduction
The agricultural industry, a vital pillar of the global economy, faces numerous challenges that hinder its growth and sustainability. Traditional methods are often plagued by inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and vulnerability to fraud. This results in wasted resources, unfair prices for farmers, and a lack of trust between stakeholders. However, the emergence of blockchain technology offers a beacon of hope. Blockchain, with its decentralized and immutable ledger system, holds the potential to transform the agriculture industry, improving efficiency, increasing transparency, and empowering farmers.
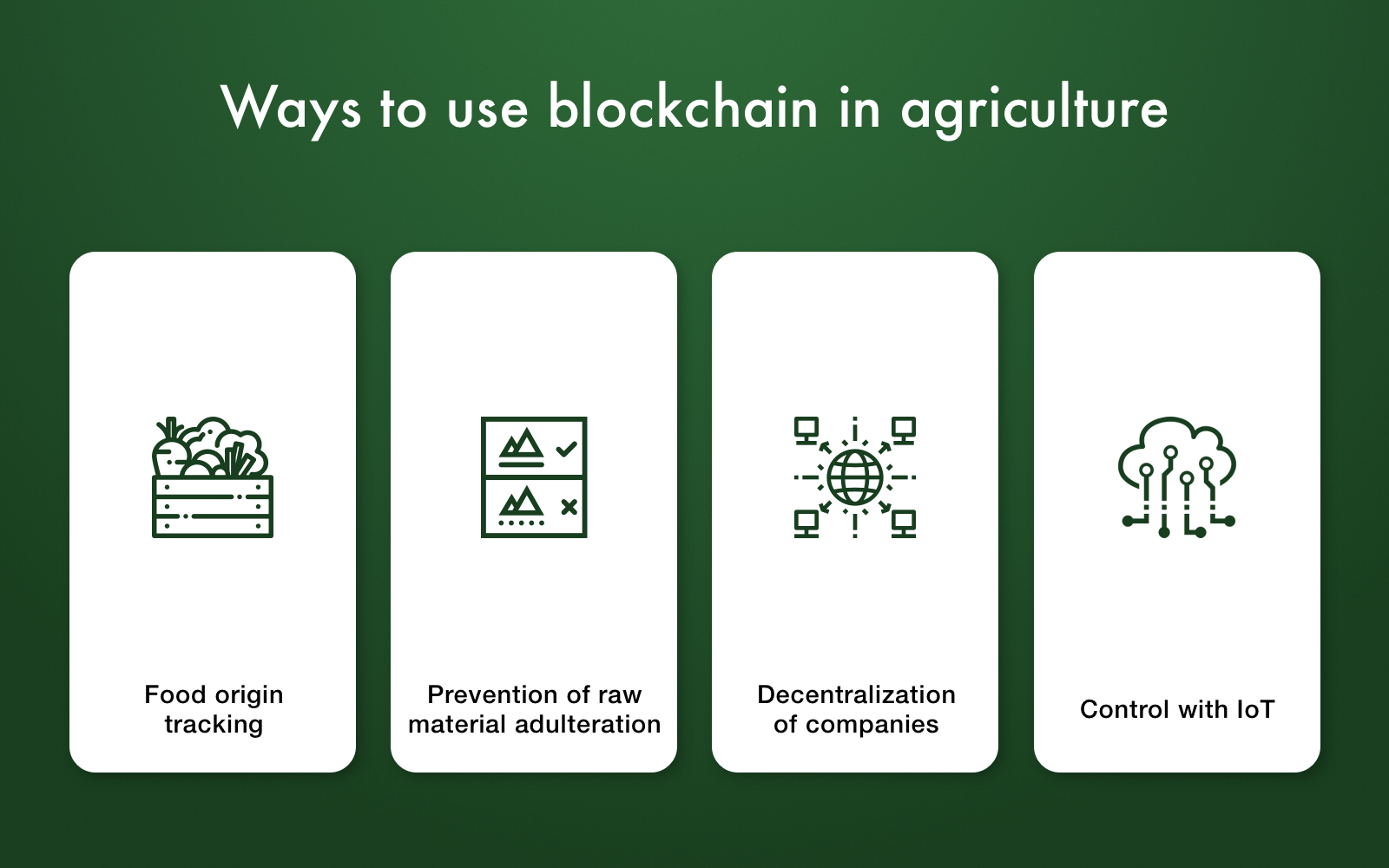
Blockchain technology allows for the creation of a secure and transparent record of transactions, making it an ideal tool for tracking food products throughout the supply chain. It can be used to trace the origin of food, ensuring its authenticity and quality, and providing consumers with greater confidence in the products they purchase. Moreover, blockchain can facilitate secure and efficient payments between farmers, suppliers, and consumers, reducing the need for intermediaries and enabling fairer pricing. This, coupled with its ability to create transparent and traceable records, can empower farmers and smallholders by giving them greater control over their products and access to new markets.
This article will explore the transformative potential of blockchain in the agricultural industry, highlighting its key applications and examining the impact it can have on various aspects of the food production and supply chain.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology offers a robust solution for enhancing transparency and traceability within the agricultural supply chain. By recording information about each stage of the food production journey – from farm to table – blockchain creates an immutable and transparent ledger that can be accessed by all stakeholders. This allows for the tracking of food products from their origin, ensuring their authenticity and quality.
- Real-time Tracking: Blockchain enables real-time tracking of food products throughout the supply chain. This data can be accessed by consumers, retailers, and regulatory authorities, providing greater transparency and accountability.
- Origin Verification: Consumers can verify the origin and authenticity of food products through blockchain-based platforms. This combats fraud and counterfeiting, building trust in the supply chain.
- Improved Food Safety: Blockchain can be used to track food safety incidents and recalls, enabling swift responses and mitigating potential health risks.
- Data Security and Integrity: Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature ensures data security and integrity, preventing tampering and manipulation of records.
Financial Inclusion and Access to Credit
Financial inclusion is a major challenge for farmers, particularly in developing countries. Blockchain can play a crucial role in improving access to credit and financial services for farmers.
- Smart Contracts for Secure Transactions: Blockchain enables the creation of smart contracts that automate financial transactions, facilitating efficient and secure payments between farmers and buyers.
- Decentralized Lending Platforms: Blockchain-based platforms can connect farmers with lenders directly, reducing the need for intermediaries and enabling easier access to loans.
- Improved Payment Systems: Blockchain can facilitate faster and more secure payments for agricultural commodities, eliminating delays and reducing costs.
- Financial Transparency and Accountability: Blockchain provides a transparent and auditable record of financial transactions, promoting accountability and reducing corruption.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Blockchain can contribute to the adoption of sustainable agriculture practices by enabling efficient resource management, tracking environmental impact, and incentivizing eco-friendly farming methods.
- Carbon Footprint Monitoring: Blockchain can track the carbon footprint of agricultural products, providing valuable data for environmental impact assessments and promoting sustainable practices.
- Resource Management and Optimization: Blockchain can track water usage, fertilizer application, and other resource inputs, enabling farmers to optimize resource allocation and reduce waste.
- Traceability of Organic Products: Blockchain can track organic certifications and ensure the authenticity of organic products, boosting consumer confidence and supporting sustainable farming.
- Rewarding Sustainable Practices: Blockchain can facilitate the creation of reward systems that incentivize farmers to adopt sustainable practices and earn rewards for their efforts.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts, a key feature of blockchain technology, automate agreements and processes, streamlining agricultural operations and eliminating the need for manual intervention.
- Contract Enforcement: Smart contracts ensure automatic contract execution based on predefined conditions, minimizing disputes and enhancing efficiency.
- Automated Payments: Smart contracts facilitate automated payments for agricultural products, reducing administrative burdens and enabling faster settlements.
- Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can automate various aspects of the supply chain, such as scheduling deliveries, tracking shipments, and managing inventory.
- Data Sharing and Collaboration: Smart contracts can enable secure and transparent data sharing between different stakeholders, fostering collaboration and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology holds immense potential to revolutionize the agricultural industry by addressing long-standing challenges and enabling sustainable growth. From enhancing supply chain transparency and traceability to facilitating financial inclusion and promoting sustainable practices, blockchain empowers farmers, improves efficiency, and builds trust within the food system.
While challenges such as scalability and regulatory frameworks remain, the transformative power of blockchain is undeniable. By embracing this technology, the agricultural industry can achieve greater efficiency, transparency, and sustainability, leading to a more robust and equitable food system that benefits both farmers and consumers.
As blockchain continues to evolve, its applications in the agricultural sector are expected to expand further. From empowering farmers with greater control over their products to providing consumers with reliable information about the origin and quality of their food, blockchain has the potential to create a more sustainable, equitable, and secure future for the global food system.
