The Latest Developments In Blockchain-based Voting Systems
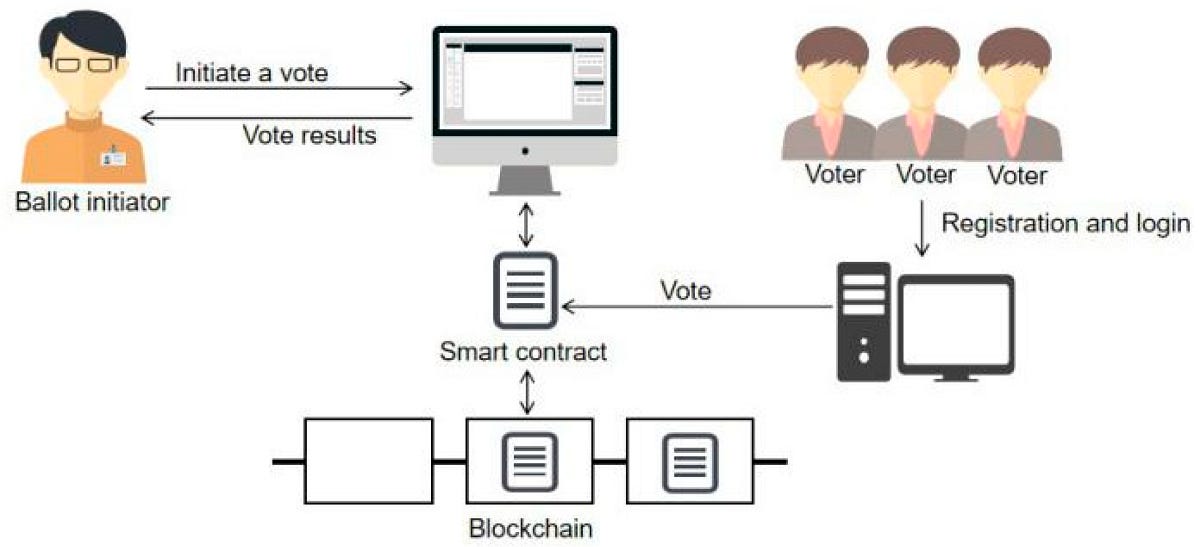
The landscape of elections is rapidly changing, with blockchain emerging as a potentially transformative force. Blockchain-based voting systems hold the promise of greater security, transparency, and accessibility, while addressing concerns surrounding traditional voting methods. This article delves into the latest advancements in blockchain-based voting systems, exploring their key features, benefits, and ongoing challenges.

Introduction

For decades, concerns about election integrity have plagued democratic societies. Issues such as voter fraud, manipulation of results, and lack of transparency have eroded public trust in the electoral process. Blockchain technology, with its inherent immutability and decentralized nature, has emerged as a potential solution to address these concerns. Blockchain-based voting systems aim to create a more secure, transparent, and accessible voting experience.
These systems leverage the principles of cryptography and distributed ledgers to record and verify votes, eliminating the need for centralized authorities. This decentralized approach enhances transparency and accountability, as all transactions are publicly auditable. Moreover, the immutability of blockchain ensures that votes cannot be altered or tampered with, enhancing trust and confidence in the electoral process.
Secure and Transparent Voting
Blockchain-based voting systems prioritize security and transparency by leveraging the robust features of blockchain technology.
- Cryptography: Cryptographic algorithms are employed to secure votes and ensure their integrity. Encryption safeguards sensitive information, while digital signatures verify the authenticity of voters and their ballots.
- Immutability: Once a vote is cast and recorded on the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This eliminates the possibility of vote tampering and ensures the integrity of the electoral process.
- Decentralization: Blockchain-based systems distribute voting records across multiple nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority. This decentralization prevents single points of failure and reduces the risk of manipulation.
- Auditability: Public ledgers provide a transparent and auditable trail of all voting activities. This allows for verification of vote counts and the identification of any potential irregularities.
Enhanced Accessibility and Convenience
Blockchain-based voting systems offer enhanced accessibility and convenience for voters, expanding participation in the electoral process.
- Remote Voting: Blockchain technology facilitates secure remote voting, enabling individuals to cast their ballots from anywhere with internet access. This empowers voters who are unable to physically visit polling stations due to mobility issues, travel restrictions, or other factors.
- Improved Usability: Blockchain-based systems often feature user-friendly interfaces that simplify the voting process. Voters can navigate through the system easily and cast their ballots with confidence.
- Increased Voter Engagement: Increased accessibility and convenience provided by blockchain systems can contribute to higher voter turnout by reducing barriers to participation.
Addressing Scalability and Privacy Concerns
While blockchain-based voting systems offer numerous benefits, they also face challenges related to scalability and privacy.
- Scalability: Blockchain networks can face limitations in processing large volumes of transactions, particularly during high-volume events like elections. This can lead to delays in vote counting and processing, impacting the efficiency of the electoral process.
- Privacy: Ensuring voter privacy in blockchain-based systems is crucial. Public ledgers can potentially expose sensitive voting data, requiring robust privacy-enhancing techniques to protect voter identities and voting choices.
- Technical Expertise: Implementing and maintaining blockchain-based voting systems requires specialized technical expertise. This can create barriers for smaller jurisdictions or those with limited resources.
Implementation and Adoption
Blockchain-based voting systems are still in their early stages of development and adoption. Several factors influence the implementation and success of these systems.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Clear regulatory frameworks are essential to establish legal and ethical guidelines for the use of blockchain-based voting systems. Governments and regulatory bodies need to address issues related to data protection, security, and election integrity.
- Public Awareness: Public awareness and understanding of blockchain technology are crucial for gaining widespread acceptance of blockchain-based voting systems. Educational initiatives and transparent communication can help build trust and confidence in these systems.
- Pilot Projects and Demonstrations: Pilot projects and demonstrations are essential for testing the feasibility and effectiveness of blockchain-based voting systems in real-world settings. These trials can help identify and address potential challenges and refine the technology.
Conclusion
Blockchain-based voting systems hold immense potential for revolutionizing the electoral process. By enhancing security, transparency, and accessibility, these systems can address longstanding concerns about election integrity and foster greater public trust in democratic institutions.
However, challenges related to scalability, privacy, and technical expertise need to be addressed effectively to ensure the successful implementation and adoption of these systems. Ongoing research, development, and collaboration among stakeholders are crucial for overcoming these obstacles and harnessing the transformative power of blockchain technology for a more secure and democratic future.