What Is Blockchain?
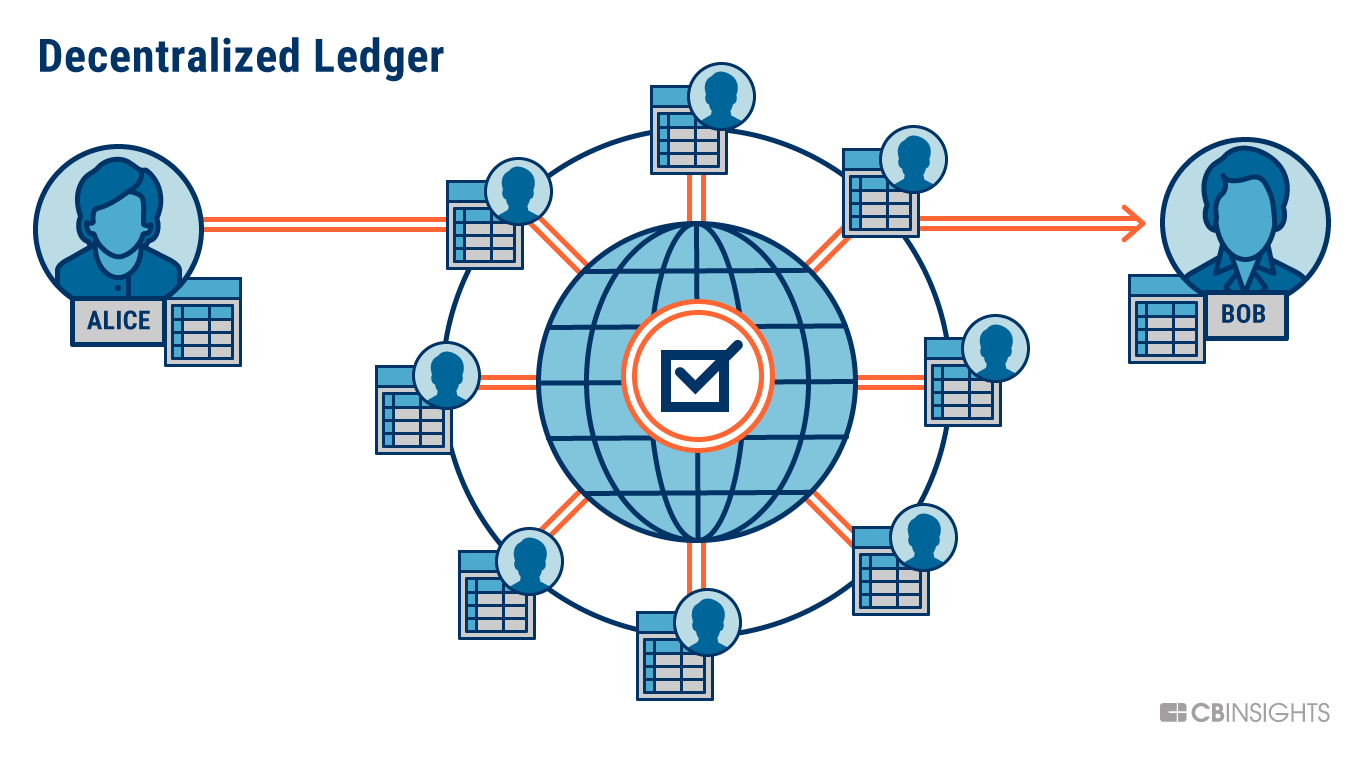
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary distributed ledger that has the potential to transform various industries, from finance to healthcare. It’s a secure, transparent, and efficient system for recording and verifying transactions. While the concept might seem complex, understanding the fundamentals of blockchain can help you appreciate its significance and potential impact on the future.

Introduction

Imagine a digital ledger shared among a network of computers. Each transaction is recorded on this ledger in a block, and these blocks are linked together in a chain, creating a permanent and immutable record. This is the essence of blockchain.
This technology has gained significant momentum in recent years due to its ability to enhance security, efficiency, and transparency in various applications. From cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to supply chain management and digital identity solutions, blockchain is finding its way into numerous sectors.
This article will delve into the key aspects of blockchain technology, exploring its core principles, functionalities, and potential applications.
Decentralization
At its core, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, meaning no single entity controls the system. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority, such as a bank or government, to oversee transactions.
- Distributed Ledger: Blockchain utilizes a distributed ledger, where copies of the ledger are held by multiple participants in the network. This ensures data redundancy and prevents manipulation by any single party.
- No Single Point of Failure: The decentralized nature eliminates the risk of a single point of failure. Even if some nodes in the network fail, the blockchain remains operational.
- Transparency and Auditability: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, making them publicly auditable. This transparency fosters trust and accountability within the network.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures data integrity and prevents fraud.
Cryptography
Blockchain heavily relies on cryptography to secure and verify transactions. Cryptography ensures data privacy, integrity, and authenticity.
- Hashing: Each block on the blockchain is assigned a unique hash value, a cryptographic function that converts data into a fixed-size string of characters. Any alteration to the data will result in a different hash, making tampering readily detectable.
- Digital Signatures: Transactions are digitally signed using public and private key pairs, ensuring authenticity and non-repudiation.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain uses consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake, to ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain.
- Encryption: Blockchain uses encryption to protect sensitive information, ensuring data privacy and confidentiality.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain, automatically enforcing agreements between parties. These contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries and ensure the timely and accurate execution of agreements.
- Automation: Smart contracts automate processes and reduce manual intervention, improving efficiency and minimizing errors.
- Transparency and Trust: All contract terms are publicly available on the blockchain, fostering transparency and trust among parties.
- Reduced Risk: Smart contracts eliminate the risk of fraud and disputes by automatically enforcing the agreed-upon terms.
- Programmability: Smart contracts can be programmed to handle complex transactions and agreements, offering flexibility and adaptability.
Applications
Blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications across various industries.
- Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain is the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It enables secure and transparent transactions between users.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency and traceability by tracking goods and materials as they move through the supply chain.
- Digital Identity: Blockchain can be used to create secure and verifiable digital identities, eliminating the need for physical documents and reducing fraud.
- Healthcare: Blockchain can improve healthcare data security and privacy by securely storing and sharing medical records.
- Voting: Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent platform for voting, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing voter confidence.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a transformative force with the potential to revolutionize numerous industries. Its decentralized nature, secure cryptography, and smart contract capabilities offer numerous benefits, including increased transparency, efficiency, and trust. While the technology is still evolving, it has already made significant strides in various sectors, and its impact is likely to grow in the coming years.
As we move forward, it is essential to understand the implications of blockchain technology and its potential to address current challenges and create new opportunities. By embracing this technology responsibly and ethically, we can harness its power to build a more secure, efficient, and equitable future.